distribution of box plot A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples. In this Instructable I'm going to walk you through how to make one of these simple sheet metal boxes! If you are just beginning to work with sheet metal I recommend also checking out my two previous sheet metal Instructables. They cover how to make SHEET METAL DOG TAGS and SHEET METAL VISE JAW COVERS.
0 · when are box plots used
1 · mean median mode box plot
2 · jmp box plot explanation
3 · interquartile box plot
4 · interpret box and whisker plot
5 · how to interpret box plot
6 · how to analyze box plots
7 · box plot minimum and maximum
It’s recommended to use a .023- or .024-inch wire for most light gauge sheet metal work. When the material is 18-gauge and thicker, you may be able to use a .030-inch wire. To weld mild steel, choose an American Welding Society classification wire such as ER70S-6, which has a weld puddle that wets out nicely.
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary .Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .First, the box plot enables statisticians to do a quick graphical examination on one or more data sets. Box-plots also take up less space and are therefore particularly useful for comparing distributions between several groups or sets of data in .
A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and .Use a box and whisker plot when the desired outcome from your analysis is to understand the distribution of data points within a range of values. They also help you determine the existence of outliers within the dataset. What is a box plot? A box plot shows the distribution of data for a continuous variable. How are box plots used? Box plots help you see the center and spread of data. You can also use them as a visual tool to check for .
Box plots are a valuable tool in statistics for visualizing the distribution of data. Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
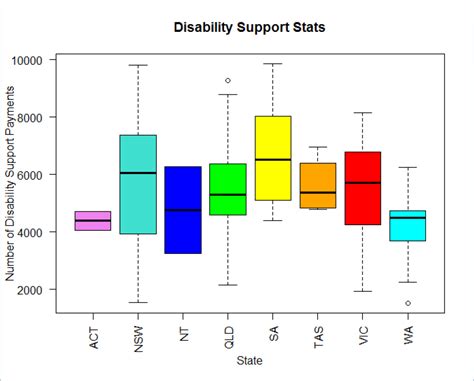
when are box plots used
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .First, the box plot enables statisticians to do a quick graphical examination on one or more data sets. Box-plots also take up less space and are therefore particularly useful for comparing distributions between several groups or sets of data in parallel (see Figure 1 for an example). A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data.
Use a box and whisker plot when the desired outcome from your analysis is to understand the distribution of data points within a range of values. They also help you determine the existence of outliers within the dataset. What is a box plot? A box plot shows the distribution of data for a continuous variable. How are box plots used? Box plots help you see the center and spread of data. You can also use them as a visual tool to check for normality or to identify points that may be outliers. Is a box plot the same as a box-and-whisker plot? Yes.
Box plots are a valuable tool in statistics for visualizing the distribution of data. Understanding how to interpret box plots can provide valuable insights into the variability and distribution of a dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk you through the key components of box plots and show you how to interpret them effectively.
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .First, the box plot enables statisticians to do a quick graphical examination on one or more data sets. Box-plots also take up less space and are therefore particularly useful for comparing distributions between several groups or sets of data in parallel (see Figure 1 for an example). A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data.Use a box and whisker plot when the desired outcome from your analysis is to understand the distribution of data points within a range of values. They also help you determine the existence of outliers within the dataset.
What is a box plot? A box plot shows the distribution of data for a continuous variable. How are box plots used? Box plots help you see the center and spread of data. You can also use them as a visual tool to check for normality or to identify points that may be outliers. Is a box plot the same as a box-and-whisker plot? Yes.
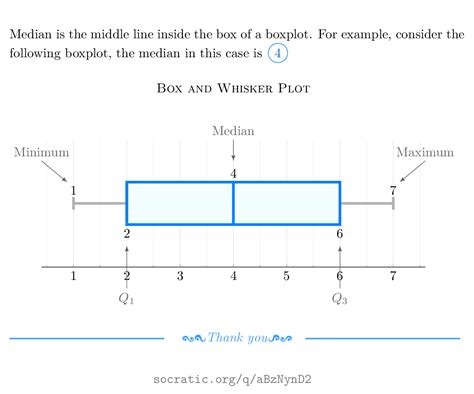
mean median mode box plot
Tie-downs, hold-downs and other requirements must be installed or performed exactly as shown in the Shop Print, with no substitutions for fastener size, spacing or embedment. Variations .
distribution of box plot|mean median mode box plot