box and whisker shape of distribution Boxplots are drawn as a box with a line inside of it, and has extended lines attached to each of its sides (known as “whiskers”). The box is used to represent the . It depends on what you are patching. 18 gauge is very close to the original thickness of the body parts. I use 18 gauge or old original body parts for large patches.
0 · symmetrical box distribution
1 · how to find box distribution
2 · difference between box and whiskers
3 · box vs whisker plot
4 · box plot skewed distribution
5 · box and whiskers explained
6 · box and whiskers chart
7 · box and whisker plot example
Metal fabricators follow patterns and blueprints to create structures from raw metal. They are skilled craftspeople who assemble structural metal products such as frameworks or shells for machinery, ovens, tanks, stacks and metal parts for buildings and bridges.
symmetrical box distribution
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
how to find box distribution
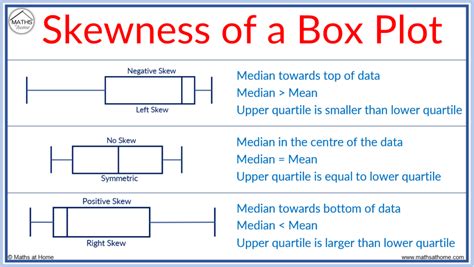
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the . Boxplots are drawn as a box with a line inside of it, and has extended lines attached to each of its sides (known as “whiskers”). The box is used to represent the .
What is a box plot? A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central .Use a box and whisker plot to show the distribution of data within a population. They allow for users to determine where the majority of the points land at a glance. They are even more useful when comparing distributions between . To make a box plot, we draw a box from the first to the third quartile. Then we draw a vertical line at the median. Lastly, we draw “whiskers” from the quartiles to the minimum and maximum value.
A boxplot, also called a box and whisker plot, is a graph that shows the dispersion and central tendency of a dataset using a five number summary. The dispersion — a measure of how spread out a data set is — includes quartiles and the .
The lengths of the whiskers and the location of the median with respect to the center of the box are used to describe the distribution of the data. It's important to note that this is just an example.Box and whisker plots are a type of graph used to visualize the distribution of data. They offer a quick and informative way to understand several key aspects of your data set. So, let's see what box and whisker plots show: Spread of the .
difference between box and whiskers
box vs whisker plot
stainless steel mosaic tile backsplash worth white cabinets
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages.
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .Boxplots are drawn as a box with a line inside of it, and has extended lines attached to each of its sides (known as “whiskers”). The box is used to represent the interquartile range (IQR) — or the 50 percent of data points lying above the first quartile and .
What is a box plot? A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.Use a box and whisker plot to show the distribution of data within a population. They allow for users to determine where the majority of the points land at a glance. They are even more useful when comparing distributions between members of a category in your data.
To make a box plot, we draw a box from the first to the third quartile. Then we draw a vertical line at the median. Lastly, we draw “whiskers” from the quartiles to the minimum and maximum value.A boxplot, also called a box and whisker plot, is a graph that shows the dispersion and central tendency of a dataset using a five number summary. The dispersion — a measure of how spread out a data set is — includes quartiles and the interquartile range. The lengths of the whiskers and the location of the median with respect to the center of the box are used to describe the distribution of the data. It's important to note that this is just an example.
Box and whisker plots are a type of graph used to visualize the distribution of data. They offer a quick and informative way to understand several key aspects of your data set. So, let's see what box and whisker plots show: Spread of the data: The box shows middle 50% of the data, with the median value dividing the box in half. In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages.A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset.
We can determine whether or not a distribution is skewed based on the location of the median value in the box plot. When the median is closer to the bottom of the box and the whisker is shorter on the lower end of the box, the distribution is right .Boxplots are drawn as a box with a line inside of it, and has extended lines attached to each of its sides (known as “whiskers”). The box is used to represent the interquartile range (IQR) — or the 50 percent of data points lying above the first quartile and .What is a box plot? A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with a central line marking the median value.
Use a box and whisker plot to show the distribution of data within a population. They allow for users to determine where the majority of the points land at a glance. They are even more useful when comparing distributions between members of a category in your data.
To make a box plot, we draw a box from the first to the third quartile. Then we draw a vertical line at the median. Lastly, we draw “whiskers” from the quartiles to the minimum and maximum value.
A boxplot, also called a box and whisker plot, is a graph that shows the dispersion and central tendency of a dataset using a five number summary. The dispersion — a measure of how spread out a data set is — includes quartiles and the interquartile range. The lengths of the whiskers and the location of the median with respect to the center of the box are used to describe the distribution of the data. It's important to note that this is just an example.
box plot skewed distribution
box and whiskers explained
^This. Beads and bends will add stiffness, so you can use thinner metal compared to a mostly flat sheet with little or no support underneath. I used 16 gage flat sheet for a 24" x 43" trunk floor, but have two u-channel supports 12" apart in the center, and two smaller right angle iron pieces to help support the outer 18" or so.
box and whisker shape of distribution|box and whiskers chart