how to describe the distribution of a box plot A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with . Leave it alone so the kind utility workers can service it when needed. Or, they’ll service it and tear out whatever you put there! It’s also right next to a gas line. Gas and buried electric, so be mindful if you do put something which requires digging, like a fence or plants.
0 · understanding box plots for dummies
1 · how to make a box and whisker plot
2 · different types of box plots
3 · describing shape of box plots
4 · boxplot shape of distribution
5 · box plot for normal distribution
6 · box plot distribution interpretation
7 · box and whisker chart type
Our guess is that is why there needs to be a small plastic piece in the iPhone 12's otherwise metal frame – to aid in the transfer of data using millimeter waves. Learn more about 5G support on the iPhone 12 here .
understanding box plots for dummies
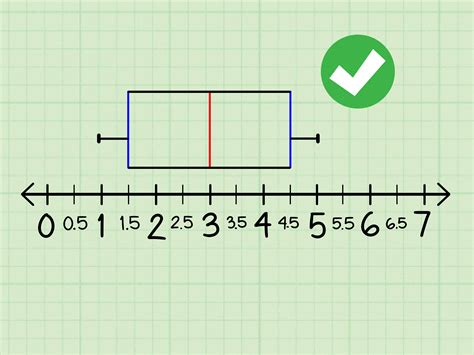
A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary .
A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum.
china aerospace cnc machining pricelist
A box plot (aka box and whisker plot) uses boxes and lines to depict the distributions of one or more groups of numeric data. Box limits indicate the range of the central 50% of the data, with . A box plot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a dataset based on a five-number summary: minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and maximum. It provides a. A box plot chart visualizes the distribution of a dataset using five key statistics: minimum, Q1, median, Q3, and maximum. It’s an efficient way to identify outliers and . Box plots provide basic information about a distribution. For example, a distribution with a positive skew would have a longer whisker in the positive direction than in the negative direction. A larger mean than median .
A boxplot is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five number summary (“minimum”, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and “maximum”). . A box plot, or the more technical term “box plot,” is a graphical representation that depicts numerical data through their quartiles. It highlights the median, range, and outliers within a dataset, providing a visual summary of .
A box plot is a type of plot that displays the five number summary of a dataset, which includes:. The minimum value; The first quartile (the 25th percentile) The median value; The third quartile (the 75th percentile) The maximum value; To make a box plot, we first draw a box from the first to the third quartile.About; Statistics; Number Theory; Java; Data Structures; Cornerstones; Calculus; Shape, Center, and Spread of a Distribution. A population parameter is a characteristic or measure obtained by using all of the data values in a population.. A sample statistic is a characteristic or measure obtained by using data values from a sample.. The parameters and statistics with which we .
From the stem plot it should be easy to describe the distribution of the data. You should be able to identify the range, the median, the quartiles, as well as any potential outliers. Finally, the stem plot should also give you an . Box Plot is a graphical method to visualize data distribution for gaining insights and making informed decisions. Box plot is a type of chart that depicts a group of numerical data through their quartiles. . All of the property of box plot can be accessed by dataframe.column_name.describe() function. Aspects of a box plot Here is a well . The direction in which you stretch the distribution is the direction of the skew. Image Source: Wikimedia Commons. When a distribution is skewed, the mean will be pulled towards the tail. The halfway point of the distribution (the median) will also fall off the peak in the direction of the tail but not as far as the mean.A box plot is a diagram used to display the distribution of data. A box plot indicates the position of the minimum, maximum and median values along with the position of the lower and upper quartiles. . Both the range and interquartile range are used to describe the spread of data. The larger the range, the more spread the whole data is.
A box plot is a diagram which summaries the key features of a data set using just 5 key values. These can be found easily once the values are arranged in order. The 5 values to be identified are Box Plot is a graphical method to visualize data distribution for gaining insights and making informed decisions. Box plot is a type of chart that depicts a group of numerical data through their quartiles. In this article, we are going to discuss components of a box plot, how to create a box plot, uses of a Box Plot, and how to compare box plots. T
How to read a box plot/Introduction to box plots. Box plots are drawn for groups of W@S scale scores. They enable us to study the distributional characteristics of a group of scores as well as the level of the scores. . Same median, different distribution – See examples (1), (2), and (3). The medians (which generally will be close to the .
How to interpret a box plot? A box plot gives us a basic idea of the distribution of the data. IF the box plot is relatively short, then the data is more compact. If the box plot is relatively tall, then the data is spread out. The interpretation of the compactness or spread of the data also applies to each of the 4 sections of the box plot.
A box plot is a type of plot that displays the five number summary of a dataset, which includes: The minimum value; The first quartile (the 25th percentile) The median value; The third quartile (the 75th percentile) The maximum value; We use the following process to draw a box plot: Draw a box from the first quartile (Q1) to the third quartile (Q3) In a box plot, it is represented by the width of the box, which ranges from the first quartile (Q1) to the third quartile (Q3) Often we create multiple box plots on one plot to compare the distribution of several datasets at once. The following example shows how to compare the variability between several box plots in practice. A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, is a graph of the five-number summary of a data set. This graph has two components. The first is a box marking off the 1st quartile (25th percentile), 2nd quartile (the median), and 3rd quartile (75th percentile) of the data.Describe how to use box plots to represent distribution of data. Create a box plot. So far you’ve looked at a number of ways to see distributions of variables. In this unit, you learn about another important graph, called a box plot. Introduced in the 1970s by American mathematician John Tukey, box plots are a visually concise way of seeing .

A larger mean than median would also indicate a positive skew. Box plots are good at portraying extreme values and are especially good at showing differences between distributions. However, many of the details of a distribution are not revealed in a box plot; to examine these details one should create a histogram and/or a stem-and-leaf display. To interpret the box plot, it really kind of depends on what you have. The most important part to interpreting outputs is to know your data. Just from what I can see in the image, I would mention the high number of outliers .Shape. The dot plot that TinkerPlots™ provides is a very useful plot. 9 It allows us to summarize the shape of the distribution very easily. Shape is used to describe a distribution’s symmetry. As you might expect, symmetric distributions are shaped the same on either side of the center.
A plot of the data is therefore essential. Open the . In the Y variable list box, . Speed. Click Calculate. The results are calculated and the analysis report opens. The histogram of the data shows a normal distribution except for two outliers. Next topic: Estimating the population mean. Tutorials; Distribution tutorial The interquartile range the median the lower and upper quartiles and the extreme minimum and. In this lesson you will learn about the shape of the distribution of data by looking at various graphs. Box Plots Box plots also called box-and-whisker plots or box-whisker plots give a good graphical image of the concentration of the data.
A box plot is a type of plot that displays the five number summary of a dataset, which includes:. The minimum value; The first quartile (the 25th percentile) The median value; The third quartile (the 75th percentile) The maximum value; To make a box plot, we first draw a box from the first to the third quartile.This type of plot simply graphs the distribution of each of the variables in a scatterplot separately in the margins, as shown in the example below. In this graph, you can see that the distribution of the variable on the X axis (horizontal) is right skewed while the distribution for the variable on the Y axis (vertical) is fairly symmetrical.
A box plot, or the more technical term “box plot,” is a graphical representation that depicts numerical data through their quartiles. It highlights the median, range, and outliers within a dataset, providing a visual summary of the distribution and variability of the data at a glance. A Q-Q plot, short for “quantile-quantile” plot, is used to assess whether or not a set of data potentially came from some theoretical distribution.. In most cases, this type of plot is used to determine whether or not a set of data follows a normal distribution. As a rule of thumb, the more that the points in a Q-Q plot lie on a straight diagonal line, the more normally distributed .
Below is a skewed distribution shown as a histogram and a boxplot. You can see the median value of the boxplot is accurate and the quartile markers (the edges of the 'box') show the skew. The outliers also indicate a skew. However, the median value doesn't indicate the expected value since the distribution isn't anywhere near normal. The .
A box plot is a type of plot that displays the five number summary of a dataset, which includes:. The minimum value; The first quartile (the 25th percentile) The median value; The third quartile (the 75th percentile) The maximum value; To make a box plot, we draw a box from the first to the third quartile.What is a box plot? A box plot is a data visualization tool that shows the distribution of data. It is an excellent tool for showing outliers. Also referred to as a box-and-whisker graph or plot, this technique shows relationships between a numerical y-variable and a grouping x-variable by using the five number summary—minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), maximum.Box Plots. We have already discussed techniques for visually representing data (see histograms and frequency polygons). In this section, we present another important graph, called a box plot. Box plots are useful for identifying outliers (extreme scores) and for comparing distributions. We will explain box plots with the help of data from an in .
china aluminum hinges for indoor door cnc machining parts
Which five-axis machining technology is right for your job shop? First, consider the parts. Then, look at existing processes and potential five-axis benefits.
how to describe the distribution of a box plot|different types of box plots