comparing distributions box and whisker In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize . 2 gang, draft tight, electrical outlet box, 36 CUIN, 3-1/2"L x 3-1/4"W x 3-1/4"D, Angled side nails for mounting for use with Non-Metallic sheathed cable, high strength polycarbonate withstands temperature extremes, meets energy efficiency requirements for new homes, features a 1/2" offset flange to ensure a flush fit in 1/2" drywall, foam .
0 · symmetrical box distribution
1 · right skewed distribution box
2 · how to find box distribution
3 · difference between box and whiskers
4 · box vs whisker plot
5 · box vs whisker chart
6 · box and whiskers explained
7 · box and whisker plot example
The steps to install a vanity light junction box include turning off the power, removing the old light fixture, installing the junction box, connecting the wires, mounting the new light fixture, and testing the connections.
When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median .
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. .In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize .Box plots are at their best when a comparison in distributions needs to be performed between groups. They are compact in their summarization of data, and it is easy to compare groups .Box and whisker plots are a powerful tool for visually understanding the distribution of data. They offer a quick and informative way to see the spread of the data, identify outliers, and compare data sets from different groups.
Use a box and whisker plot to show the distribution of data within a population. They allow for users to determine where the majority of the points land at a glance. They are even more useful when comparing distributions between .
In other words, Box and Whisker Plots are a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary (minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile .Calculation of range and median along with Box-and-whisker plots and Cumulative frequency tables are effective ways to compare distributions and to summarise their characteristics.
weatherproof electrical box fittings
symmetrical box distribution
Comparing distributions can be much more interesting than just describing a single distribution. of a distribution reports its median, quartiles, and extremes (maximum and minimum). Consists . When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format. In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages.
In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.Box plots are at their best when a comparison in distributions needs to be performed between groups. They are compact in their summarization of data, and it is easy to compare groups through the box and whisker markings’ positions.
Box and whisker plots are a powerful tool for visually understanding the distribution of data. They offer a quick and informative way to see the spread of the data, identify outliers, and compare data sets from different groups.Use a box and whisker plot to show the distribution of data within a population. They allow for users to determine where the majority of the points land at a glance. They are even more useful when comparing distributions between members of a category in your data.
In other words, Box and Whisker Plots are a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary (minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and “maximum”). Some important terms relevant for obtaining these five numbers are –. Median – The middle value of the dataset.Calculation of range and median along with Box-and-whisker plots and Cumulative frequency tables are effective ways to compare distributions and to summarise their characteristics.
Comparing distributions can be much more interesting than just describing a single distribution. of a distribution reports its median, quartiles, and extremes (maximum and minimum). Consists of the minimum value, Q1, the median, Q3, and the maximum value, listed in that order. Offers a reasonably complete description of the center and spread. When comparing two or more box plots, we can answer four different questions: 1. How do the median values compare? We can compare the vertical line in each box to determine which dataset has a higher median value. 2. How does the dispersion compare?A box plot, sometimes called a box and whisker plot, provides a snapshot of your continuous variable’s distribution. They particularly excel at comparing the distributions of groups within your dataset. A box plot displays a ton of information in a simplified format.
In descriptive statistics, a box plot or boxplot (also known as a box and whisker plot) is a type of chart often used in explanatory data analysis. Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages.In this explainer, we will learn how to compare two data set distributions using box plots. Box plots, which are sometimes called box-and-whisker plots, can be a good way to visualize differences among groups that have been measured on the same variable.Box plots are at their best when a comparison in distributions needs to be performed between groups. They are compact in their summarization of data, and it is easy to compare groups through the box and whisker markings’ positions.Box and whisker plots are a powerful tool for visually understanding the distribution of data. They offer a quick and informative way to see the spread of the data, identify outliers, and compare data sets from different groups.
Use a box and whisker plot to show the distribution of data within a population. They allow for users to determine where the majority of the points land at a glance. They are even more useful when comparing distributions between members of a category in your data.In other words, Box and Whisker Plots are a standardized way of displaying the distribution of data based on a five-number summary (minimum, first quartile (Q1), median, third quartile (Q3), and “maximum”). Some important terms relevant for obtaining these five numbers are –. Median – The middle value of the dataset.Calculation of range and median along with Box-and-whisker plots and Cumulative frequency tables are effective ways to compare distributions and to summarise their characteristics.
weather resistant electrical enclosure 24x4x4
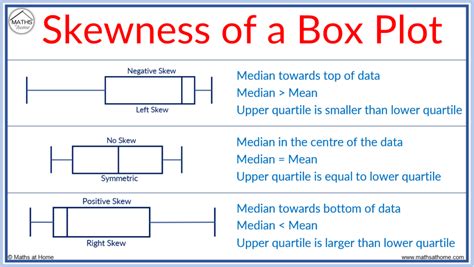
right skewed distribution box
wd sheet metal minneapolis minnesota
how to find box distribution
The Red Hook Stores complex at the end of Van Brunt Street is now home to a Fairway Market. Originally known as the New York Warehouse Co.’s Stores, this structure dates back to the 1870s.
comparing distributions box and whisker|box vs whisker plot