cnc machine for helicopter rotor blades 1940 Parsons is an exceedingly interesting case study of how industrial and engineering supply firms—in this case, Parsons notably made ordnance casings and fins in World War II, then helicopter rotor blades in the 1940s, '50s, and . Realise your projects precisely and quickly with modern CNC machines from vhf. No matter if you want to mill plastics, aluminum, non-ferrous metals, wood or if you want to cut soft materials – with the vhf milling machines you will get a suitable machining option for almost any material.
0 · REMEMBERING JOHN T PARSONS A BRIEF TIMELINE
1 · REMEMBERING JOHN T PARSONS
2 · John T. Parsons History Project
3 · John T. Parsons
4 · John T Parsons
5 · History of CNC Machining — James Engineering
6 · Computer Pioneers
7 · About: John T. Parsons
This L-shaped folk victorian style farmhouse design features a white exterior color that contrasts nicely with the coral orange roofing shingles (find out more on our homestead metal roofing shades). The simplified vergeboard paired with the scalloped shingles creates a modest structure with ornate detailing.
John T. Parsons (October 11, 1913 – April 18, 2007) pioneered numerical control (NC) for machine tools in the 1940s. These developments were done in collaboration with his Chief Engineer .

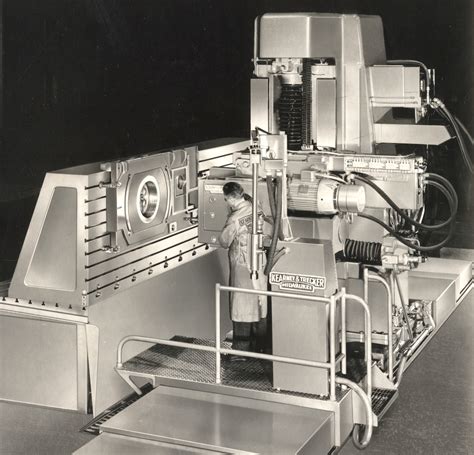
4-axis N/C machine tool for helicopter rotor blades. 1965 Participated in the blade design and designed and developed the manufacturing process and tooling for the world's first tapered .Conceived and directed the installation of a special 4-axis N/C machine tool for helicopter rotor blades. Participated in the blade design and conceived the manufacturing process and tooling for the first tapered metal helicopter rotor . For 40 years, he worked at Parsons Corporation, which became a world leader in production of helicopter blades, and produced fuel tanks for the .Parsons is an exceedingly interesting case study of how industrial and engineering supply firms—in this case, Parsons notably made ordnance casings and fins in World War II, then helicopter rotor blades in the 1940s, '50s, and .
John T. Parsons (October 11, 1913 – April 18, 2007) pioneered numerical control (NC) for machine tools in the 1940s. These developments were done in collaboration with his Chief Engineer .His company had made a number of manufacturing innovations in producing land mines, bombs, rockets, and helicopter rotor blades during World War 11. In 1947 he and Frank Stulen .
Their origins can be traced back to the 1940s and a man named John Parsons. Parsons was an engineer who initially started working for Sikorsky Aircraft building helicopter rotor blades, but when they started to fall, he knew he had .Together, they were the first to use computer methods to solve machining problems, in particular, the accurate interpolation of the curves describing helicopter rotor blades. In the 1940s, a ‘computer’ meant a punch card .
Together, they were the first to use computer methods to solve machining problems, in particular, the accurate interpolation of the curves describing helicopter rotor blades. In 1946, "computer" still meant a punched .
John T. Parsons (October 11, 1913 – April 18, 2007) pioneered numerical control (NC) for machine tools in the 1940s. These developments were done in collaboration with his Chief Engineer and Vice President of Engineering, Frank L. Stulen , who Parsons hired when he was head of the Rotary Wing Branch of the Propeller Lab at Wright-Patterson .4-axis N/C machine tool for helicopter rotor blades. 1965 Participated in the blade design and designed and developed the manufacturing process and tooling for the world's first tapered metal helicopter rotor blade (Lockheed AH-56 helicopter). Not even one blade was said to have been scrapped during the entire program. 1967Conceived and directed the installation of a special 4-axis N/C machine tool for helicopter rotor blades. Participated in the blade design and conceived the manufacturing process and tooling for the first tapered metal helicopter rotor blade (Lockheed AH-56 helicopter). Not even one blade was scrapped during the entire program.
For 40 years, he worked at Parsons Corporation, which became a world leader in production of helicopter blades, and produced fuel tanks for the Saturn rockets that took astronauts to the moon. Parsons’s breakthroughs in computerized manufacturing led to the development of Computer Numerical Control (CNC), which controls the automation of .Parsons is an exceedingly interesting case study of how industrial and engineering supply firms—in this case, Parsons notably made ordnance casings and fins in World War II, then helicopter rotor blades in the 1940s, '50s, and '60s (which is where he developed numerical control [NC] machining), and eventually fiberglass boats for the leisure .John T. Parsons (October 11, 1913 – April 18, 2007) pioneered numerical control (NC) for machine tools in the 1940s. These developments were done in collaboration with his Chief Engineer and Vice President of Engineering, Frank L. Stulen, who Parsons hired when he was head of the Rotary Wing Branch of the Propeller Lab at Wright-Patterson Air .His company had made a number of manufacturing innovations in producing land mines, bombs, rockets, and helicopter rotor blades during World War 11. In 1947 he and Frank Stulen developed a method to produce contoured templets for checking blades by calculating successive machine positions on an IBM multiplier and then manually setting the .
Their origins can be traced back to the 1940s and a man named John Parsons. Parsons was an engineer who initially started working for Sikorsky Aircraft building helicopter rotor blades, but when they started to fall, he knew he had to find a better solution to building them.Together, they were the first to use computer methods to solve machining problems, in particular, the accurate interpolation of the curves describing helicopter rotor blades. In the 1940s, a ‘computer’ meant a punch card-operated calculation machine. Together, they were the first to use computer methods to solve machining problems, in particular, the accurate interpolation of the curves describing helicopter rotor blades. In 1946, "computer" still meant a punched-card operated calculation machine.John T. Parsons (October 11, 1913 – April 18, 2007) pioneered numerical control (NC) for machine tools in the 1940s. These developments were done in collaboration with his Chief Engineer and Vice President of Engineering, Frank L. Stulen , who Parsons hired when he was head of the Rotary Wing Branch of the Propeller Lab at Wright-Patterson .
4-axis N/C machine tool for helicopter rotor blades. 1965 Participated in the blade design and designed and developed the manufacturing process and tooling for the world's first tapered metal helicopter rotor blade (Lockheed AH-56 helicopter). Not even one blade was said to have been scrapped during the entire program. 1967Conceived and directed the installation of a special 4-axis N/C machine tool for helicopter rotor blades. Participated in the blade design and conceived the manufacturing process and tooling for the first tapered metal helicopter rotor blade (Lockheed AH-56 helicopter). Not even one blade was scrapped during the entire program.
For 40 years, he worked at Parsons Corporation, which became a world leader in production of helicopter blades, and produced fuel tanks for the Saturn rockets that took astronauts to the moon. Parsons’s breakthroughs in computerized manufacturing led to the development of Computer Numerical Control (CNC), which controls the automation of .Parsons is an exceedingly interesting case study of how industrial and engineering supply firms—in this case, Parsons notably made ordnance casings and fins in World War II, then helicopter rotor blades in the 1940s, '50s, and '60s (which is where he developed numerical control [NC] machining), and eventually fiberglass boats for the leisure .John T. Parsons (October 11, 1913 – April 18, 2007) pioneered numerical control (NC) for machine tools in the 1940s. These developments were done in collaboration with his Chief Engineer and Vice President of Engineering, Frank L. Stulen, who Parsons hired when he was head of the Rotary Wing Branch of the Propeller Lab at Wright-Patterson Air .His company had made a number of manufacturing innovations in producing land mines, bombs, rockets, and helicopter rotor blades during World War 11. In 1947 he and Frank Stulen developed a method to produce contoured templets for checking blades by calculating successive machine positions on an IBM multiplier and then manually setting the .

Their origins can be traced back to the 1940s and a man named John Parsons. Parsons was an engineer who initially started working for Sikorsky Aircraft building helicopter rotor blades, but when they started to fall, he knew he had to find a better solution to building them.
REMEMBERING JOHN T PARSONS A BRIEF TIMELINE
Together, they were the first to use computer methods to solve machining problems, in particular, the accurate interpolation of the curves describing helicopter rotor blades. In the 1940s, a ‘computer’ meant a punch card-operated calculation machine.
steel kitchen cabinets manufacturers in hyderabad

Find helpful customer reviews and review ratings for Home Depot Vigoro 3-in-1 Metal Deck Plant Bracket, Planter Box Hanger, Holds 30 lbs at Amazon.com. Read honest and unbiased product reviews from our users.
cnc machine for helicopter rotor blades 1940|About: John T. Parsons