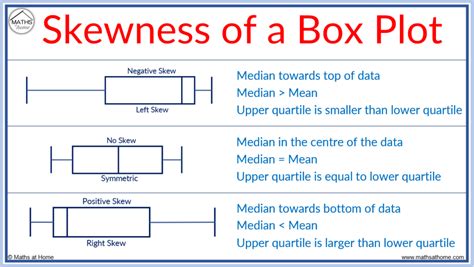
box plot distribution shapes Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a . CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that employs computerized controls and machine tools to remove layers of material from a stock piece, known as the blank or workpiece, to produce a custom-designed part 1.
0 · symmetric box and whisker plot
1 · skewness on a box plot
2 · skewed box and whisker plot
3 · shape of distribution skewed right
4 · shape of distribution skewed left
5 · right skewed data box plot
6 · right skewed box plot vertical
7 · explain box plot with example
A PV junction box is an enclosure on the solar PV module where the PV strings are electrically connected. The output cables usually carry MC4 connectors.
symmetric box and whisker plot
Compare the respective medians of each box plot. If the median line of a box plot lies outside of the box of a comparison box plot, then there is likely to be a difference between the two groups. Source: https://blog.bioturing.com/2018/05/22/how-to-compare-box-plots/ See moreCompare the interquartile ranges (that is, the box lengths) to examine how the data is dispersed between each sample. The longer the box, the . See moreWhen reviewing a box plot, an outlier is defined as a data point that is located outside the whiskers of the box plot. See more
A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.
Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a .
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .Box plots truly shine when comparing data distributions across different groups. Their compact design offers a neat summary of data, making it a breeze to compare distributional properties of the groups through the positioning of box .A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, .
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed .
A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and .When a data set is graphed, each point is arranged to produce one of dozens of different shapes. The distribution shape can give you a visual which helps to show how the data is: Spread out (e.g. dispersion , variability , scatter ),
Using the five number summary, one can construct a skeletal boxplot. Mark the five number summary above the horizontal axis with vertical lines. Connect Q 1, Q 2, Q 3 to form a box, then connect the box to min and max with a line to form . Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.Box plots truly shine when comparing data distributions across different groups. Their compact design offers a neat summary of data, making it a breeze to compare distributional properties of the groups through the positioning of box and whisker markings.

skewness on a box plot
A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data.When a data set is graphed, each point is arranged to produce one of dozens of different shapes. The distribution shape can give you a visual which helps to show how the data is: Spread out (e.g. dispersion , variability , scatter ),
Using the five number summary, one can construct a skeletal boxplot. Mark the five number summary above the horizontal axis with vertical lines. Connect Q 1, Q 2, Q 3 to form a box, then connect the box to min and max with a line to form the whisker.
Box plots visually show the distribution of numerical data and skewness by displaying the data quartiles (or percentiles) and averages. Box plots show the five-number summary of a set of data: including the minimum score, first (lower) quartile, median, third (upper) quartile, and maximum score.A box plot is an easy method to display the set of data distribution in terms of quartiles. Visit BYJU’S to learn its definition, and learn how to find out the five-number summary of box plot with Examples.Box plots are used to show distributions of numeric data values, especially when you want to compare them between multiple groups. They are built to provide high-level information at a glance, offering general information about a group of .Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right.
Box plots truly shine when comparing data distributions across different groups. Their compact design offers a neat summary of data, making it a breeze to compare distributional properties of the groups through the positioning of box and whisker markings.A boxplot, also known as a box plot, box plots, or box-and-whisker plot, is a standardized way of displaying the distribution of a data set based on its five-number summary of data points: the “minimum,” first quartile [Q1], median, third quartile [Q3] and “maximum.”
Histograms and box plots can be quite useful in suggesting the shape of a probability distribution. Here, we'll concern ourselves with three possible shapes: symmetric, skewed left, or skewed right. A box plot, also known as a box-and-whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the distribution of a dataset. It summarizes key statistics such as the median, quartiles, and outliers, providing insights into the spread and central tendency of the data.When a data set is graphed, each point is arranged to produce one of dozens of different shapes. The distribution shape can give you a visual which helps to show how the data is: Spread out (e.g. dispersion , variability , scatter ),
You can find the gauge to mm / inch conversion for sheet metal by the chart below. Or you can Download the Sheet Metal Gauge Size Chart PDF. (Click here) How many mm is 8 gauge? For different materials of steel, the same gauge will also correspond to different mm. What is 10 gauge in mm? What is 16 gauge thickness in mm?
box plot distribution shapes|right skewed data box plot